Arctic Sea Ice Nears Historic Low: Antarctic Decline Continues
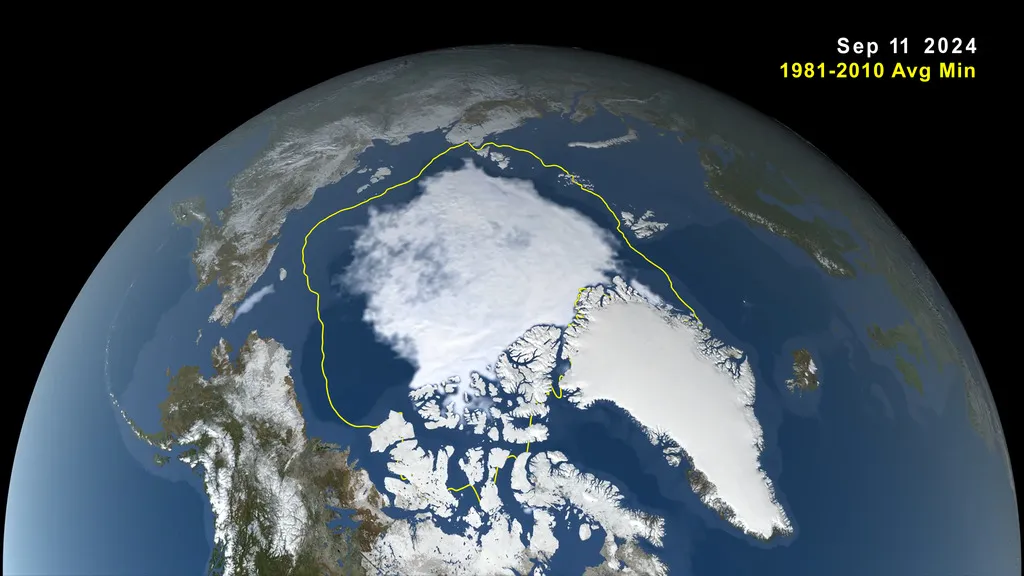
A Troubling Trend in Arctic Ice
his summer, Arctic sea ice reached near-record lows, hitting its annual minimum on September 11, 2024. NASA and the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) highlight that this ongoing decline reflects decades of shrinking and thinning ice in the Arctic Ocean.
Seasonal variations in Arctic sea ice include thawing and regrowth, but satellite data over the past 46 years reveal a troubling trend: increased summer melting and reduced winter formation. This raises significant concerns about the Arctic’s vulnerability to rising temperatures and extended melting seasons.
Significant Changes and Consequences
This year, Arctic sea ice shrank to 1.65 million square miles (4.28 million square kilometers), about 750,000 square miles (1.94 million square kilometers) below the 1981–2010 average of 2.4 million square miles (6.22 million square kilometers)—an area larger than Alaska.
While this extent is above the record low of 2012, it ranks as the seventh-lowest since the late 1970s. The Arctic loses roughly 30,000 square miles (77,800 square kilometers) of ice annually, underscoring the persistent effects of climate change.
Scientists use advanced satellite technology to track sea ice extent and thickness. Nathan Kurtz from NASA notes that much of the current ice is younger and thinner, making it less resilient to warmth. Research shows that older, thicker ice has significantly declined; fall sea ice in the central Arctic now averages about 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) thick, down from 8.8 feet (2.7 meters) in 1980. This thinning threatens both the Arctic ecosystem and global weather patterns.
Broader Implications for Life and Trade
The decline of Arctic sea ice has far-reaching consequences, from disrupting polar wildlife habitats to threatening the livelihoods of local communities dependent on ice. Additionally, changes in ice cover are reshaping international shipping routes, increasing accessibility but raising environmental concerns.
Ongoing monitoring provides valuable data on the planet’s health, guiding policies to combat climate change. The alarming reduction in Arctic ice underscores the urgent need for action against global warming.
Through advanced satellite observations and research, scientists aim to deepen our understanding of Arctic sea ice dynamics and their global significance. The critical state of both Arctic and Antarctic ice calls for sustained global attention and action.
Related News
More News
Latest News

Maharashtra assembly election result 2024 latest update

US Military Launches Strikes on 15 Key Houthi Targets in Yemen

Putin’s Nuclear Doctrine Shake-Up: A Game Changer for Global Tensions

Maldivian President Mohamed Muizzu Set for Key Diplomatic Visit to India, October 6-10

Iran’s Leader Justifies Strikes on Israel in Powerful, Rare Public Address